Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
Eigenvalues and eigenvectors are important in dynamic problems
Introduction
Suppose we have a Matrix $A$. What does it do with a vector?
- Suppose we multiply $A$ by a vector $\mathbf x$ - and we get a vector $A \mathbf x$
- what if $A \mathbf x$ is in the same direction as $\mathbf x$?
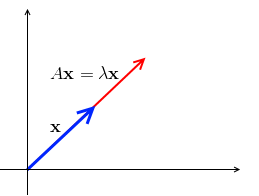
- i.e. if it’s the same direction, then $A \mathbf x = \lambda \mathbf x$ for some $\lambda$
- such $\mathbf x$ is called ‘‘eigenvector’’ and $\lambda$ is called ‘‘eigenvalue’’
What if $\lambda = 0$?
- $A \mathbf x = 0 \mathbf x = \mathbf 0$
- i.e. $\mathbf x \in N(A)$ - the eigenvector $\mathbf x$ belongs to the Nullspace
- so if $A$ is singular, then $\lambda = 0$ is its eigenvalue
Example: Projection Matrices
Sometimes we can find the eigenvalues by thinking geometrically
- suppose we have a Projection Matrix $P$
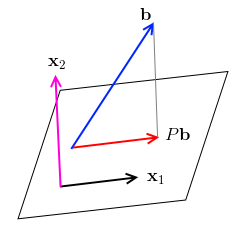
- for a vector $\mathbf b$ that’s not on the place formed by $C(P)$, $\mathbf b$ is not an eigenvector - $P \mathbf b$ is a projection, so they point to different directions
- suppose there’s a vector $\mathbf x_1$ on the plane. $P \mathbf x_1 = \mathbf x_1$, so all such $\mathbf x_1$ on the plane are eigenvectors with eigenvalues $\lambda = 1$
- are there other eigenvectors? take any $\mathbf x_2$ orthogonal to the plane: $P \mathbf x_2 = 0 \mathbf x_2 = \mathbf 0$, so $\lambda = 0$
- so we have two eigenvalues $\lambda = 0$ and $\lambda = 1$
Solving $A \mathbf x = \lambda \mathbf x$
- Cannot use Gaussian Elimination here
- we have two unknowns: $\lambda$ and $\mathbf x$
$A \mathbf x = \lambda \mathbf x$
- let’s rewrite it as $(A - \lambda I) \mathbf x = \mathbf 0$
- for $\mathbf x \ne \mathbf 0$
- so the matrix $A - \lambda I$ is singular, thus its Determinant is zero:
- $\text{det}(A - \lambda I) = 0$ - this is called the ‘‘characteristic equation’’
- this equation has $n$ roots, so you’ll find $n$ eigenvalues $\lambda_i$
- then for each $\lambda_i$ we solve the system $A \mathbf x = \lambda_i \mathbf x$ in order to get eigenvectors
$(A - \lambda I) \mathbf x = \mathbf 0$ This eigenvectors are in the Nullspace of $(A - \lambda I)$
Eigenvalues are sometimes called “singular values” because if $\lambda$ is an eigenvalue, then $A - \lambda I$ is singular
Example
Example 1
Let $A = \begin{bmatrix}
3 & 1
1 & 3
\end{bmatrix}$
- $\text{det}(A - \lambda I) = \begin{bmatrix}
3 - \lambda & 1
1 & 3- \lambda
\end{bmatrix} = (3 - \lambda)^2 - 1 = 0$ - or $(3 - \lambda)^2 = 1$
- $3 - \lambda = \pm 1$
- $\lambda_1 = 4, \lambda_2 = 2$
Now can find eigenvectors
- $(A - \lambda_1 I) \mathbf x_1 = (A - 4 I) \mathbf x_1 = 0$, so $x_1 = \begin{bmatrix} 1 \ 1 \end{bmatrix} \in N(A - 4 I)$
- $(A - \lambda_2 I) \mathbf x_2 = (A - 2 I) \mathbf x_2 = 0$, so $x_2 = \begin{bmatrix} -1 \ 1 \end{bmatrix} \in N(A - 2 I)$
Example 2: Rotation Matrix
Let $Q = \begin{bmatrix}
0 & -1
1 & 0
\end{bmatrix}$
- know that $\text{tr } Q = \sum_i \lambda_i$, so $\lambda_1 + \lambda_2 = 0$
- $\text{det } Q = \lambda_1 \, \lambda_2 = 1$
- how it’s possible?
- $\text{det } Q = \begin{vmatrix}
-\lambda & -1
1 & -\lambda
\end{vmatrix} = \lambda^2 + 1$ - so $\lambda_1 = i$ and $\lambda_2 = -i$ - complex numbers
- note that they are complex conjugates
- this doesn’t happen for Symmetric matrices - they always have real eigenvalues
Properties
Gaussian Elimination changes the eigenvalues of $A$
- Triangular $U$ has its eigenvalues on the diagonal - but they are not eigenvalues of $A$
eigenvectors can be multiplied by any non-negative constant and will still remain eigenvectors
- so it’s good to make these vectors unit vectors
Trace and Determinant
$\text{tr } A = \sum\limits_i \lambda_i$
- $\text{tr } A$ is a Trace of $A$
$\text{det } A = \prod\limits_i \lambda_i$
- $\text{det } A$ is a Determinant of $A$
Eigenvectors and Eigenvalues of $A^k$
if $A \mathbf x = \lambda \mathbf x$ then
- $A^2 \mathbf x = \lambda A \mathbf x = \lambda^2 \mathbf x$
- so $\lambda$s are squared when $A$ is squared
- the eigenvectors stay the same
- For $A^k$ the eigenvalues are $\lambda_i^k$
- Eigenvectors stay the same and don’t mix up, only eigenvalues grow
Linear Independence
If all eigenvalues $\lambda_1, \ … \ , \lambda_n$ are different then all eigenvectors $\mathbf x_1, \ … \ , \mathbf x_n$ are linearly independent
- so any matrix with distinct eigenvalues can be diagonalized
’'’Thm.’’’ $\mathbf x_1, \ … \ , \mathbf x_n$ that correspond to distinct eigenvalues are linearly independent.
Proof
- Let $\mathbf x_1, \mathbf x_2, \ … \ , \mathbf x_n$ be eigenvectors of some matrix $A$ (so none of them are $\mathbf 0$)
- and also assume that eigenvalues are distinct, i.e. $\lambda_1 \ne \lambda_2 \ne \ … \ \ne \lambda_n$
$n = 2$ case:
- consider a linear combination $c_1 \mathbf x_1 + c_2 \mathbf x_2 = \mathbf 0$
- multiply it by $A$:
- $c_1 A \, \mathbf x_1 + c_2 A \, \mathbf x_2 = c_1 \lambda_1 \mathbf x_1 + c_2 \lambda_1 \mathbf x_2 = \mathbf 0$
- then multiply $c_1 \mathbf x_1 + c_2 \mathbf x_2 = \mathbf 0$ by $\lambda_2$:
- $c_1 \lambda_2 \mathbf x_1 + c_2 \lambda_2 \mathbf x_2 = \mathbf 0$
- subtract equation 1 from 2 to get the following:
- $(\lambda_1 - \lambda_2) c_1 \mathbf x_1 = \mathbf 0$
- since $\lambda_1 \ne \lambda_2$ and $x_1 \ne \mathbf 0$, so it means that $c_1 = 0$
- by similar argument we see that $c_2 = 0$
- thus $c_1 \mathbf x_1 + c_2 \mathbf x_2 = \mathbf 0$ because $c_1 = c_2 = 0$
- or, $\mathbf x_1$ and $\mathbf x_2$ are linearly independent
General case:
- consider $c_1 \mathbf x_1 + \ … \ + c_n \mathbf x_n = \mathbf 0$
- multiply by $A$ to get $c_1 \lambda_1 \mathbf x_1 + \ … \ + c_n \lambda_n \mathbf x_n = \mathbf 0$
- multiply by $\lambda_n$ to get $c_1 \lambda_n \mathbf x_1 + \ … \ + c_n \lambda_n \mathbf x_n = \mathbf 0$
- subtract them, get $\mathbf x_n$ removed and have the following:
- $c_1 (\lambda_1 - \lambda_n) \mathbf x_1 + \ … \ + c_{n - 1} (\lambda_{n - 1} - \lambda_n) \mathbf x_{n - 1} = \mathbf 0$
- do the same again: multiply it with $A$ and with $\lambda_{n-1}$ to get
- $c_1 (\lambda_1 - \lambda_n) \lambda_1 \mathbf x_1 + \ … \ + c_{n - 1} (\lambda_{n - 1} - \lambda_n) \lambda_{n - 1} \mathbf x_{n - 1} = \mathbf 0$
- $c_1 (\lambda_1 - \lambda_n) \lambda_{n - 1} \mathbf x_1 + \ … \ + c_{n - 1} (\lambda_{n - 1} - \lambda_n) \lambda_{n - 1} \mathbf x_{n - 1} = \mathbf 0$
- subtract to get rid of $\mathbf x_{n - 1}$
- eventually, have this:
- $(\lambda_1 - \lambda_2) \cdot (\lambda_1 - \lambda_3) \cdot \ … \ \cdot (\lambda_1 - \lambda_{n}) \cdot c_1 \mathbf x_{n} = \mathbf 0$
- since all $\lambda_i$ are distinct and $x_{n} \ne \mathbf 0$, conclude that $c_1 = 0$
- can show the same for the rest $c_2, \ … \ , c_n$
- thus $\mathbf x_1, \mathbf x_2, \ … \ , \mathbf x_n$ are linearly independent
$\square$
Eigenvector Matrix
Suppose we have $n$ linearly independent eigenvectors $\mathbf x_i$ of $A$
- let’s put them in columns of a matrix $S$ - eigenvector matrix
$S = \Bigg[ \mathop{\mathbb x_1}\limits_| ^| \ \mathop{\mathbb x_2}\limits_|^| \ \cdots \ \mathop{\mathbb x_n}\limits_|^| \Bigg]$ | This matrix is used for Matrix Diagonalization
Usage
- Matrix decomposition: Eigendecomposition (Spectral Theorem) and SVD
- Eigenvectors give a good basis, especially for Symmetric Matrices: they are orthogonal
- Principal Component Analysis
- Markov Chains and PageRank
- many many others
Sources
- Linear Algebra MIT 18.06 (OCW)
- Strang, G. Introduction to linear algebra.