== Hyperbolic Trigonometric Functions == Hyperbolic trigs are analogs of usual Trigonometric Functions
- $\cosh x = \cfrac{e^x + e^{-x}}{2}$
- $\sinh x = \cfrac{e^x - e^{-x}}{2}$
- $\tanh x = \cfrac{\sinh x}{\cosh x} = \cfrac{e^x - e^{-x}}{e^x + e^{-x}}$
 (source: [http://calculus.seas.upenn.edu/?n=Main.ComputingTaylorSeries])
(source: [http://calculus.seas.upenn.edu/?n=Main.ComputingTaylorSeries])
- $\cosh^2 x - \sinh^2 x = 1$
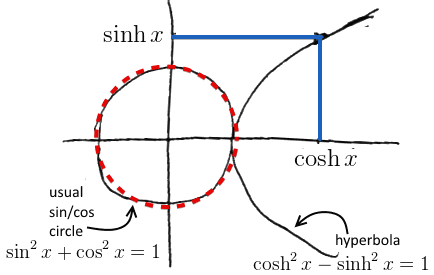
Taylor Expansion:
- $\cosh x = \cfrac{e^x + e^{-x}}{2} = \cfrac{1}{2}\, e^x + \cfrac{1}{2}\, e^{-x} = \ …$
-
$… \ = \cfrac{1}{2}\, \left(1 + x + \cfrac{1}{2 }\, x^2 + \cfrac{1}{3!}\, x^3 + \ … \ \right) + \cfrac{1}{2}\, \left(1 - x + \cfrac{1}{2!}\, x^2 - \cfrac{1}{3!}\, x^3 + \ … \ \right) = \ …$ - odd degree terms cancel out - $… \ = 1 + \cfrac{1}{2 }\, x^2 + + \cfrac{1}{4!}\, x^4 + \ … \ = \sum\limits_{k=0}^\infty \cfrac{x^2}{(2k)!}$ - co we have even powers, like for $\cos x$, just without $(-1)^k$ term - same for $\sinh x = \cfrac{1}{2}\, e^x - \cfrac{1}{2}\, e^{-x} = \sum\limits_{k=0}^\infty \cfrac{x^{2k + 1}}{(2k+1) }$ - if we Taylor expand $e^x$, even powers cancel out, and we’re left only with odd powers - just like usual $\sin x$, but without alternating sing
-
Derivatives
- $\cfrac{d}{dx}\, \sinh x = \cosh x$
- $\cfrac{d}{dx}\, \cosh x = \sinh x$
Can show that with Taylor expansions:
-
$\cfrac{d}{dx}\, \sinh x = \cfrac{d}{dx} \sum\limits_{k=0}^\infty \cfrac{x^{2k + 1}}{(2k+1) } = \sum\limits_{k=0}^\infty (2k+1)\, \cfrac{x^{2k}}{(2k+1)!} = \sum\limits_{k=0}^\infty \cfrac{x^{2k}}{(2k)!} = \cosh x$ - same with $\cosh x$