OWL
OWL - Web Ontology Language
Several languages
- OWL-Full - No limits, but some things can be undecidable
- OWL-DL - Descriptive Logic
- OWL-Lite - RDFS-Plus, DL-Lite
- for logical semantics behind there expressions see Semantic Web Logic
owl:Restriction: Restrictions
Allows to describe classes in terms of other things we already modeled
- a Restriction in OWL is a Class defined by describing the individuals it contains
owl:Restriction rdfs:subClassOf owl:Class
Kinds of Restrictions
owl:someValuesFrom- all individuals form which at least one value of the property $P$ comes from some class $C$
- e.g.
:AllStarPlayeris a:Playerfor which at least one value of:playsForcomes from the class:AllStarTeam [a owl:Restiction; owl:onProperty :playsFor; owl:someValuesFrom :AllStarTeam]- if at least one team of this guy is of the class
:AllStarTeam$\Rightarrow$ he is an:AllStarPlayer
owl:allValuesFrom- individuals for which all values of property $P$ come from class $C$
- if there are any members, they all must have the same property
owl:hasValue- all individuals that have some specific value $a$ for the property $P$
- e.g. :JapanTeams - the set of all baseball
:Teams:from :Japan - e.g. Suppose we have a property
:orbitsAround- then everything that
:orbitsAround :TheSunbelongs to the:SolarSystem [a owl:Restriction; owl:onProperty :orbitsAround; owl:hasValue :TheSun]
- then everything that
Best way to use these restrictions:
rdfs:subClassOfowl:equivalentClass
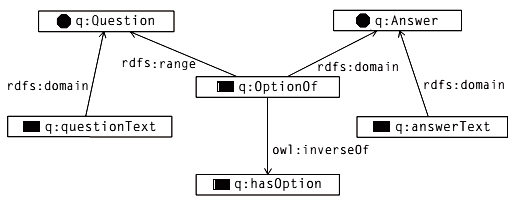
Example: Questionnaire
- a questionnaire contains a number of questions
- each question has some possible answers
- in contrast to a quiz there is no “right” answer
- the selection of some answers precludes other questions
Schema (namespace q):
```actionscript 3 q:optionOf a owl:ObjectProperty; rdfs:domain q:Answer; rdfs:range q:Question; owl:inverseOf q:hasOption. q:hasOption a owl:ObjectProperty. q:answerText a owl:DatatypeProperty; rdfs:domain q:Answer; rdfs:range xsd:string. q:questionText a owl:FunctionalProperty, owl:DatatypeProperty; rdfs:domain q:Question; rdfs:range xsd:string. q:Answer a owl:Class. q:Question a owl:Class.
Data (namespace <code>d</code>):
```actionscript 3
d:WhatProblem a q:Question;
q:hasOption d:STV, d:SInternet, d:SBoth;
q:questionText "What system are you having trouble with?".
d:STV a q:Answer;
q:answerText "Cable TV".
d:SInternet a q:Answer;
q:answerText "High-speed Internet".
d:SBoth a q:Answer;
q:answerText "Both".
d:TVsymptom a q:Question;
q:questionText "What television symptoms are you having?";
q:hasOption d:TVSnothing, d:TVSnosound, d:TVStiling, d:TVSreception.
d:TVSnothing a q:Answer;
q:answerText "No Picture".
d:TVSnosound a q:Answer;
q:answerText "No Sound".
d:TVStiling a q:Answer;
q:answerText "Tiling".
d:TVSreception a q:Answer;
q:answerText "Bad reception".
owl:someValuesFrom: Answered questions
For each question need to know what’s selected
- for that first define a special property
q:hasSelectedOption:q:hasSelectedOption a owl:ObjectProperty; rdfs:subPropertyOf q:hasOption.
- suppose that for
d:WhatProblemthe selected option isd:STVd:WhatProblem q:hasSelectedOption d:STV
- a question is answered if it has a selected option (e.g.
d:WhatProblemis answered)
q:AnsweredQuestion owl:equivalentClass
[a owl:Resrtiction;
owl:onProperty q:hasSelectedOption;
owl:someValuesFrom q:Answer].
owl:allValuesFrom: Next Questions
Next questions should depend of what’s been asked and answered
- first, define all answers that were selected
q:SelectedAnswer a owl:Class; rdfs:subClassOf q:Answer- to make sure that any option that was selected will appear in this class:
q:SelectedAnswer rdfs:range q:SelectedAnswer- e.g.
d:WhatProblem q:hasSelectedOption d:STV$\Rightarrow$ d:STV a q:SelectedAnswer
now define questions that can be asked: q:EnabledQuestion a owl:Class
- when some answer is selected, we want to infer that some dependent questions become enabled
- each answer potentially makes some other questions enabled
- define property
q:enablesCandidatefor that
```actionscript 3 q:enablesCandidate a owl:ObjectProperty; rdfs:domain q:Asnwer; rdfs:range q:Question.
d:STV q:enablesCandidate d:TVsymptom. d:SBoth q:enablesCandidate d:TVsymptom.
Restriction:
- we want that only answers that were selected enforce this property
- so use <code>owl:allValuesFrom</code> and <code>rdfs:subClassOf</code>
```objective-c
q:SelectedAnswer rdfs:subClassOf [a owl:Restriction;
owl:onProperty q:enablesCandidate;
owl:allValuesFrom q:EnabledQuestion]
Inference example
- assume
d:STVis selected:d:STV a q:SelectedAnswer - infer that
d:STV a [a owl:Restriction; owl:onProperty q:enablesCandidate; owl:allValuesFrom q:EnabledQuestion] - any individuals related to it by
q:enablesCandidatemust be members ofq:EnabledQuestion - since
d:STV q:enablesCandidate d:TVsymptominfer thatd:TVsymptom a q:EnabledQuestion
Sets and Counting
Union and Intersection
U a owl:Class; owl:unionOf (ns:A ns:B ...) .I a owl:Class; owl:intersectionOf (ns:A ns:B ...) .
Example:
- suppose we want to know what are enabled high-priority questions
q:CandidateQuestions owl:equivalentClass [ a owl:Class; owl:intersectionOf(q:EnabledQuestion q:HighPriorityQuestion)]
Set Enumeration: Closing the World
Recall the Open World Assumption (see Semantic Web#Main Assumptions)
- we can’t be sure that if we don’t have a record about some fact then it doesn’t exist:
- it can exist, but maybe we just don’t know about it
- sometimes we need to “close the world”: assume we know everything
owl:oneOf
- we assume that we can enumerate all the elements of some class
- so we put a limit on the AAA slogan: now nobody can say something additional about this topic
- so handle it with care
- Example:
actionscript 3 ss:SolarPlanet rdf:type owl:Class; owl:oneOf (ss:Mercury ss:Venus ss:Earth ss:Mars ss:Jupiter ss:Saturn ss:Uranus ss:Neptune).
Cardinality Restrictions
- to express constants on the # of individuals who can participate in some restriction class
- for example, a baseball team can have only 9 players
[a owl:Restriction;
owl:onProperty :hasPlayer;
owl:cardinality 9]
Also can use:
owl:minCardinality- lower boundowl:maxCardinality- upper bound
Set Compliment
ex:ClassA owl:complimentOf ex:ClassB
- '’compliment’’ - another class whose members are things that don’t belong to this ‘‘complimented’’ class
- $A = \Omega - B$
But it includes everything that is not in the complimented class
- e.g.
bb:MinorLeaguePlayer owl:complimentOf bb:MajorLeaguePlayer - this will include everything else in the universe: players, managers, fans, planets, etc
- solution: combine with intersection
bb:MinorLeaguePlayer owl:intersectionOf (
[a owl:Class; owl:complimentOf bb:MajorLeaguePlayer]
bb:Player)
- so
bb:MinorLeaguePlayers arebb:Players who’s not in Major League
Disjoint Sets
:Man owl:disjointSet :Woman
:Irene a :Woman:Ralph a :Man- infer that
:Irene owl:differentFRom :Ralph
Links
Protégé
- http://protege.stanford.edu/download/download.html
- useful tool for building OWL models
- good tutorial: http://owl.cs.manchester.ac.uk/tutorials/protegeowltutorial/
See Also
- RDFS and OWL Summary
- Semantic Web
- RDF
- RDFS
- RDFS-Plus - a subset of OWL and an extension of RDFS with more inferencing capabilities
- Inference in Semantic Web
- Semantic Web Logics