Vector Orthogonality
In geometry, we call two vectors $\mathbf x$ and $\mathbf y$ ‘‘orthogonal’’ of the angle between then is 90 - i.e. they are perpendicular.
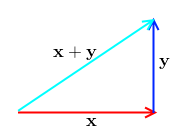
Inner Product Test
- If $\mathbf x$ and $\mathbf y$ are perpendicular, then we can use the Pythagoras theorem
-
$| \mathbf x |^2 + | \mathbf y |^2 = | \mathbf x + \mathbf y* |^2$ - is there an easier way to tell if 2 vectors are orthogonal? - yes| if their Inner Product is zero, then they are: $\mathbf x^T \mathbf y = \sum x_i y_i = 0 \Rightarrow \mathbf x \, \bot \, \mathbf y$ | | Why?
-
$| \mathbf x |^2 = \left(\sqrt{\sum x_i^2 } \right)^2 = \mathbf x^T \mathbf x$ - let’s expand the Pythagoras theorem: -
$| \mathbf x |^2 + | \mathbf y |^2 = | \mathbf x + \mathbf y* |^2$ - $\mathbf x^T \mathbf x + \mathbf y^T \mathbf y = (\mathbf x + \mathbf y)^T (\mathbf x + \mathbf y) = \mathbf x^T \mathbf x + \mathbf x^T \mathbf y + \mathbf y^T \mathbf x + \mathbf y^T \mathbf y$ - or $\mathbf x^T \mathbf y + \mathbf y^T \mathbf x = 0$
- note that $\mathbf x^T \mathbf y = \mathbf y^T \mathbf x$, so we have
- $2 \mathbf x^T \mathbf y = 0$ or $\mathbf x^T \mathbf y = 0$
Zero Vectors
Zero vectors $\mathbf 0$ are orthogonal to any vector in its space
- $\mathbf 0 \; \bot \; \mathbf x$ $\forall \mathbf x$
- because $\mathbf 0^T \mathbf x = 0$
Sources
- Linear Algebra MIT 18.06 (OCW)
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Orthogonality