Difference between revisions of "Machine Learning Diagnosis"
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
* Try adding polynomial features (beware of [[Overfitting]]!) | * Try adding polynomial features (beware of [[Overfitting]]!) | ||
* Try increasing [[Regularization|regularization parameter]] $\lambda$ | * Try increasing [[Regularization|regularization parameter]] $\lambda$ | ||
| − | * Try decreasing $\lambda $ | + | * Try decreasing $\lambda$ |
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
the main sources of problems are | the main sources of problems are | ||
* high bias (underfit) | * high bias (underfit) | ||
| + | ** tendency to constantly learn the same wrong thing | ||
| + | ** you're always missing in the same way | ||
* high variance ([[Overfitting]]) | * high variance ([[Overfitting]]) | ||
| + | ** tendency to output random things irrespective to the input data | ||
| + | ** you depend too much on the training data | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Dart throwing illustration: | ||
| + | * https://raw.githubusercontent.com/alexeygrigorev/wiki-figures/master/crs/ds/high-variance-bias.png | ||
| + | |||
| Line 48: | Line 57: | ||
* $J_{\text{train}}(\theta)$ is low, $but J_{\text{cv}}(\theta)$ is high | * $J_{\text{train}}(\theta)$ is low, $but J_{\text{cv}}(\theta)$ is high | ||
* and $J_{\text{cv}}(\theta) \gg J_{\text{train}}(\theta)$ (much greater) | * and $J_{\text{cv}}(\theta) \gg J_{\text{train}}(\theta)$ (much greater) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| Line 80: | Line 91: | ||
| − | == See | + | == See Also == |
* [[Overfitting]] | * [[Overfitting]] | ||
* [[Learning Curves]] | * [[Learning Curves]] | ||
| Line 88: | Line 99: | ||
== Sources == | == Sources == | ||
* [[Machine Learning (coursera)]] | * [[Machine Learning (coursera)]] | ||
| + | * Domingos, Pedro. "A few useful things to know about machine learning." [http://homes.cs.washington.edu/~pedrod/papers/cacm12.pdf] | ||
| + | |||
[[Category:Machine Learning]] | [[Category:Machine Learning]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Model Performance Evaluation]] | ||
Revision as of 23:26, 27 April 2017
Contents
Machine Learning Diagnosis
Suppose you created a model, but when you tested it, you found that it makes large errors
What should you try?
- Get more training examples
- Try smaller set of features
- Try getting additional features
- Try adding polynomial features (beware of Overfitting!)
- Try increasing regularization parameter $\lambda$
- Try decreasing $\lambda$
Diagnosis - a test that you can run to gain insights what is working with the learning algorithms and what is not, and gain guidance as how to improve the performance.
Evaluating a Hypothesis
To test if we overfit, we can perform Cross-Validation:
- train the model on the training set
- check the model on the test set
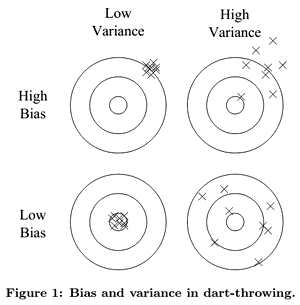
Diagnosing Bias vs Variance
the main sources of problems are
- high bias (underfit)
- tendency to constantly learn the same wrong thing
- you're always missing in the same way
- high variance (Overfitting)
- tendency to output random things irrespective to the input data
- you depend too much on the training data
Dart throwing illustration:
Fitting Polynomial
How to distinguish between them and say which one of them we experience?
- Suppose we want to fit parameter $d$ - what degree of polynomial to use (see here)
- with $d = 1$ we underfit
- with $d = 2$ we are just right
- with $d = 4$ we overfit
We can plot the cost function errors vs degree of polynomial $d$ for
- the training set $J_{\text{train}}(\theta)$
- the cross-validation (or test) set $J_{\text{cv}}(\theta)$
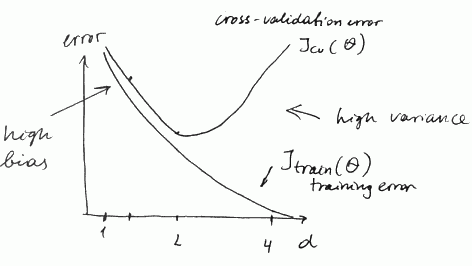
in case of bias (underfit) we have
- both $J_{\text{train}}(\theta)$ and $J_{\text{cv}}(\theta)$ are high
- and $J_{\text{train}}(\theta) \approx J_{\text{cv}}(\theta)$
in case of variance (overfit)
- $J_{\text{train}}(\theta)$ is low, $but J_{\text{cv}}(\theta)$ is high
- and $J_{\text{cv}}(\theta) \gg J_{\text{train}}(\theta)$ (much greater)
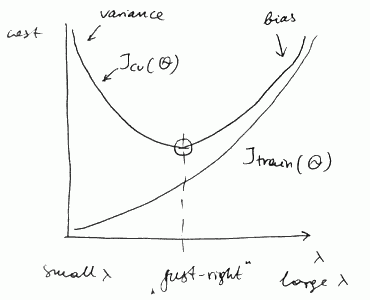
Fitting Regularization Parameter
When we try to find the best Regularization parameter for a hypothesis we get similar curves:
- with small $\lambda$ we have high variance
- with large $\lambda$ we have high bias
Learning Curves
Learning Curves is a technique that is used to
- sanity-check our algorithm or
- improve performance
- diagnose high bias (underfit)
- diagnose high variance (overfit)
What To Do Next?
So, depending on what kind of problem we have, we should decide what to do next
To fix high variance:
- Get more training examples
- Try smaller set of features
- Try decreasing regularization parameter $\lambda$
To fix high bias:
- Try getting additional features
- Try adding polynomial features (beware of Overfitting!)
- Try increasing regularization parameter $\lambda$
See Also
Sources
- Machine Learning (coursera)
- Domingos, Pedro. "A few useful things to know about machine learning." [1]