Active Databases
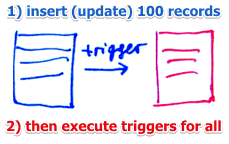
In contrast to passive databases, in active databases, execution of actions can be triggered in response to some monitored events
- database updates and inserts
- points in time
- etc
Triggers
Usually there are some rules in such databases that react on the external events
Event - Condition - Action
- when an event occurs
- if a condition holds
- then an action is performed
Example
- event: customer has not paid 3 invoices at the due date
- condition: the credit limit is less than 20k euros
- cancel all current orders of this customer
Rule Triggers
These rules are usually expressed via triggers in databases
- a trigger may cause another trigger to fire rollback - abort the transaction that caused the triggered event
Applications
Rules usually express various aspects of application semantics and are typically used for maintaining Consistency (databases)
- static constrains
- referential integrity
- value constraints
- business rules
- historical data
- like all data about complete orders should be moved to a Data Warehouse
- Management of Derived Data
Management of Derived Data
An important application of triggers in Active Databases
This includes:
- materialized attributes
- materialized views
- replicated data
Derived Data:
- '’Views’’: a query on the database that can be used as a relation in other queries
- '’Derived attributes’’: values that are computed from other values
There are two strategies for derived data
- virtually supported - computed on demand (virtual tables)
- materialized - stored in a database and must be recomputed whenever the source data changes
Semantics
Triggers are usually a part of transaction
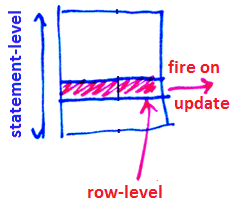
Levels of granularity
- statement-level
- executed once per statement
- row-level (or tuple-level)
- a rule is triggered line-by-line
Triggering types:
- Before triggers
- executed before the modification of a row
- in some databases (DB2) cannot modify the DB
- After triggers
- executed after the modification
- Instead-Of triggers
- when action on one table is replaced on different action
- typically used for managing derived data
Execution mode:
- deferred
- all triggered rules are put in a conflict set
- once a transaction finishes, the triggers are executed
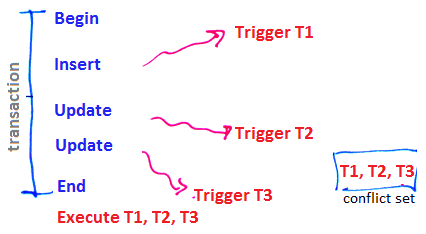
- immediate
- just after the modification
Oracle
It supports
- both row-level and row-level
- both before triggers and after triggers
Rule processing algorithm
- execute the statement-level before triggers
- for each row affected by the triggering statement
- execute the row-level before triggers
- execute the modification of the row, check constraints and assertions
- execute the row-level after triggers
- perform statement-level assertion checking
- execute statement-level after trigger
- the modification may trigger another rules
- then the execution of the current statement is suspended
- the maximum number of active triggers in a chain is 32
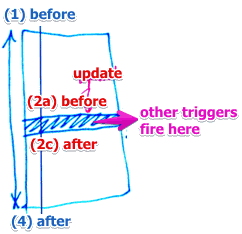
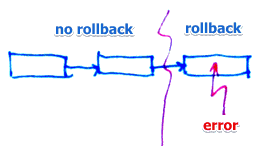
Partial rollback
- it’s possible to rollback only one statement instead of the whole transaction
MS SQL Server Triggers
The execution of triggers is immediate in MS SQL
- triggers are executed after an instruction (not after each row or each transaction)
Types:
- After: after the instruction takes place
- Instead Of: executes some custom code instead of the instruction
Syntax
```text only
CREATE TABLE |as
Inserted - new or updated rows of the triggered transaction
- Deleted - deleted rows (or rows with old state for updates) of the triggered transaction
### Examples
#### Example 1
consider the following schema:
- 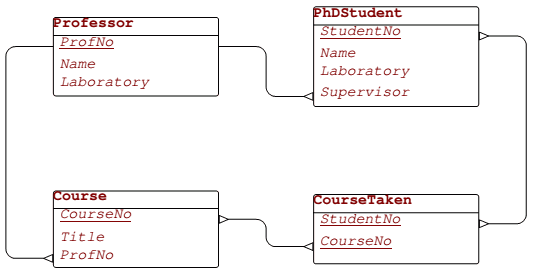 Constraint:
- PhD Students must work in the same laboratory as their supervisors
Events that may violate this constraint:
- (a) insert into
Constraint:
- PhD Students must work in the same laboratory as their supervisors
Events that may violate this constraint:
- (a) insert into PhDStudent
- (b) update of Laboratory or Supervisor in PhDStudent
- (c) update of Laboratory in Professor
- (d) delete from Professor
Events (a) and (b):
```scdoc
create trigger StudSameLabAsSuperv_PhDStud_InsUpd_Abort
-- EVENT
on PhDStudent
after insert, update
as
-- CONDITION
if exists (
select * from Inserted I, Professor P
where P.ProfNo = I.Supervisor
-- and not the same laboratory
and P.Laboratory <> I.Laboratory)
begin
-- ACTION
raiserror 13000 'Constraint Violation:
A PhD student must work in the same
laboratory as his/her supervisor'
rollback
end
```
Event (c)
```scdoc
create trigger StudSameLabAsSuperv_Prof_Upd_Abort
on Professor
after update
as
if exists (
-- if there exists a student who is supervised
-- by professor who works in different lab
select * from Inserted I, PhDStudent S
where I.ProfNo = S.Supervisor
and I.Laboratory <> S.Laboratory)
begin
raiserror 13000 'Constraint Violation:
A PhD student must work in the same
laboratory as his/her supervisor'
rollback
end
```
Event (d)
- A DBMS system will not allow this if there's a foreign key
#### Example 2
 ; The age of employees must be greater than 18
- this can be done with
; The age of employees must be greater than 18
- this can be done with CHECK constraint
```gdscript
alter table Employee
add constraint employee_Age18
check (dateadd(year, 18, BDate) <= getdate())
```
; The attribute Department.NbrEmployees is derived from Employee.DNo
- can recalculate everything
- or update incrementally
```scdoc
create trigger DeptNbrEmp_Employee_InsUpdDel_Derive
on Employee
after insert, update, delete
as
begin
update Department D
set NbrEmployees = (select Count(*)
from Employee E
where E.DNo = D.DNumber)
where D.DNumber in (select distinct I.DNo
from Inserted I)
or D.DNumber in (select distinct D.DNo
from Deleted D)
end
```
Incremental version
```scdoc
create trigger derived_Department_NbrEmployees_Employee
on Employee
after insert, update, delete
as
begin
update Department
set NbrEmployees = NbrEmployees
+ (select count(*) from Inserted I
where DNumber = I.DNo)
- (select count(*) from Deleted D
where DNumber = D.DNo)
where DNumber in (select DNo from Inserted)
or DNumber in (select DNo from Deleted)
end
```
Now also need to ensure that no one can modify this attribute
```scdoc
create trigger derived_Department_NbrEmployees_Department
on Department
after insert, update
as
if exists (select *
from Inserted
where NbrEmployees <>
(select count(*) from Employee E
where E.DNo = DNumber))
begin
raiserror 13008 'Constraint Violation:
The attribute Department.NbrEmployees is a derived attribute from Employee.DNo'
rollback
end
```
## Sources
- [Advanced Databases (ULB)](Advanced_Databases_(ULB))