Dijkstra’s Shortest Path
Goal: to find the shortest path in a graph from a single-source s
input
- directed graph $G = (V, E)$
- each edge has non-negative length
- source vertex $s$
output
- for each $v \in V$ complete
- $L(v)$ = length of the shortest path from $s$ to $v$ in $G$
Algorithm
Dijkstra’s(graph $G$, vertex $s$)
Initialization:
- $X = {s}$: vertices we’ve processed so far
- $A[s] = 0$: at the end, it’ll be populated with the shortest paths
- $B[s] = \varnothing$ (empty path): computed shortest path, or explanation only
Main loop:
- we examine all edges that came from $X$ to $V - X$
- and among all vertices we pick one which gives the minimal score in Dijkstra’s greedy criterion $A[v] + l_{vw}$: we call it ‘‘minimizing edge’’
while $X \neq V$:
- for all $(v, w) \in E$
- with $v \in X$ and $w \notin X$
- pick a pair that minimizes $A[v] + l_{vw}$ ($A[v]$ is already computed in earlier iterations)
- let the minimizing edge be $(v^, w^)$
- add $w^*$ to $X$
- $A[w^] = A[v] + l_{v^w^}$: shortest path from $s$ to $w^$
- $B[w^] = B[v^] + (v^, w^)$
Example
- $s$ - starting vertex
- <img src=”
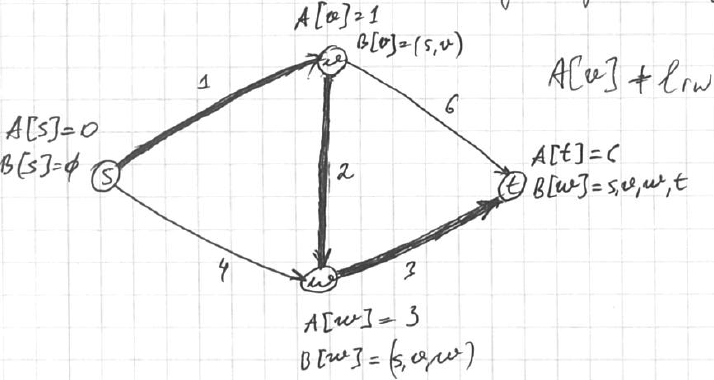 ” >
” >
Non-example
-
won’t compute the shortest path for non-negative edges - <img src=” 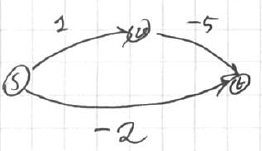 ” >
” >
Implementation notes
- don’t need the $B$ array
- $\Theta(mn)$ - naive implementation of Dijkstra’s
- with heaps - better speed
Heaps to speed up Dijkstra
invariants to keep with heaps
- elements in heap: vertices in $V - X$ (not processed)
- for $v \notin X$
- $\text{key}[v]$ = smallest Dijkstra’s greedy score of $(u, v) \in E$ with $v \in X$
- $\text{key}[v] = +\infty$ if an edge doesn’t exist
if maintain 2nd invariants
- extract-min returns vertex $w^*$ to add to $X$ next
to maintain 2nd invariant
- when we extract $w$ from heap (added to $X$)
- for each edge $(w, v) \in E$
- if $v \in V - X$ (i.e. already in the heap)
- we update the key
- delete $v$ from heap
- recompute $\text{key}[x] = \min(\text{key}[u], A[w] + l_{wv})$
- re-insert $v$ into heap
running time with heaps: $O(m \log_2 n)$
Implementation
```text only public static final int INFINITY = 1000000;
public static int[] dijkstra(UndirectedWeightedGraph graph, int s) { int dist[] = new int[graph.getN()]; Arrays.fill(dist, INFINITY);
List<HeapNode<Integer, Integer>> heapNodesList = prepareHeapNodesList(graph.getN());
Heap<Integer, Integer> heap = Heap.naturalMin();
HeapNode<Integer, Integer> sourceHeapNode = heap.insert(s, 0);
heapNodesList.set(s, sourceHeapNode);
for (int i = 0; i < graph.getN(); i++) {
if (i | = s) { | HeapNode<Integer, Integer> result = heap.insert(i, INFINITY); | heapNodesList.set(i, result);
}
}
int n = graph.getN();
while (n > 0) {
HeapNode<Integer, Integer> node = heap.extractFirst();
int distance = node.getKey();
int nodeNumber = node.getValue();
dist[nodeNumber] = distance;
for (Edge edge : graph.adjacent(nodeNumber)) {
int to = edge.getTo();
HeapNode<Integer, Integer> toNode = heapNodesList.get(to);
int newDistance = distance + edge.getWeight();
if (newDistance < toNode.getKey()) {
heap.decreaseKey(toNode, newDistance);
}
}
n--;
}
return dist; }
@SuppressWarnings(“unchecked”) private static List<HeapNode<Integer, Integer» prepareHeapNodesList(int n) { List<?> list = Arrays.asList(new HeapNode[n]); return (List<HeapNode<Integer, Integer») list; } ```
Heap implementation can be found here: Heap#Implementation
See also
Sources
- Algorithms Design and Analysis Part 1 (coursera)
- http://algorithms.soc.srcf.net/notes/dijkstra_with_heaps.pdf