Graphs
Consist of:
- vertices aka nodes ($V$)
- $n$ = number of vertices
- edges ($E$) = pair of vertices
-
$m$ - number of edges
- can be ‘‘undirected’’ <img src=”
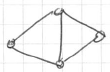 ” >
” > - or ‘‘directed’’ <img src=”
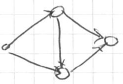 ” >
” >
Directed Acyclic Graph
This is a special kind of graph where
- there are no cycles
- and it is directed
These graphs can be sorted topologically
Representation
adjacency matrix
- $n \times n$ matrix where
- $A_{i,j} = 1$ if $G$ has $(i, j)$ edge
- or $+1$/$-1$ if directed
- or weight if weighted
- space required $\Theta(n^2)$
adjacency list
- array of vertices
- array of edges for each vertex
- space required $\Theta(n + m)$
Implementation
Adjacency list:
public class Graph {
private int n;
private final List<List<Integer>> adj;
public Graph(int n) {
this.n = n;
this.adj = createAdjacentList(n);
}
private static List<List<Integer>> createAdjacentList(int n) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(n);
int i = 0;
while (i < n) {
res.add(new LinkedList<Integer>());
i++;
}
return res;
}
public void addEdge(int v, int u) {
adj.get(v).add(u);
}
public Iterable<Integer> adjacent(int v) {
return adj.get(v);
}
public int getN() {
return n;
}
}
See also
- Minimal Cut Problem
- Graph Search (Breadth-First Search и Depth-First Search)
- Dijkstra’s Shortest Path
- Topological Ordering