Column Space
A column space $C(A)$ of a matrix $A$ is a subspace formed by columns of $A$
- it’s one of is one of the Four Fundamental Subspaces of $A$
$C(A)$
Let $A$ be $m \times n$ matrix:
-
$A = \left[ \mathop{a_1}\limits_ ^ \, \mathop{a_2}\limits_ ^ \ \cdots \ \mathop{a_n}\limits_ ^ \right]$ - the columns of $A$ form a subspace - a hyperplane through the origin 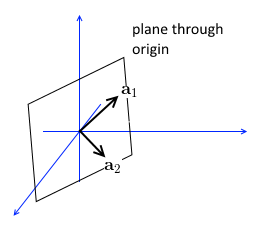
- $C(A)$ is in $\mathbb R^r$ space where $r \leqslant n$ is the $A$’s Rank
- so the dimensionality is at most the number of columns, and at least the rank of the matrix
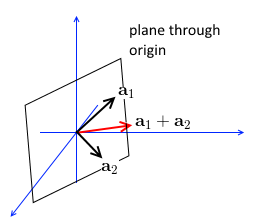
It’s a subspace:
- if we take any vectors from $C(A)$, the linear combination will still be $C(A)$ (by definition)
Example
Suppose we have a matrix $A \in \mathbb R^{3 \times 2}$
$A = \begin{bmatrix}
1 & 3
2 & 3
4 & 1
\end{bmatrix}$
Subspace from columns - $C(A)$ - the Column Space of $A$:
- we cannot just take the two columns and call it a subspace:
- it also must include all linear combinations of these columns
- these linear combinations of two vectors form a plane - a subspace $\mathbb R^2$ in the space $\mathbb R^3$
- since we include all possible combinations, we’re guaranteed to have a subspace
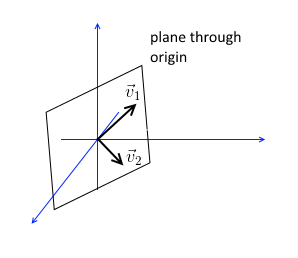
- $v_1$ and $v_2$ are 1st and 2nd columns of $A$ - they form a plane through the origin
System $A \mathbf x = \mathbf b$
Column Space $C(A)$ of $A$ is important: the system $A \mathbf x = \mathbf b$ has the solution only when $\mathbf b \in C(A)$
For example:
$A = \begin{bmatrix}
1 & 1 & 2
2 & 1 & 3
3 & 1 & 4
4 & 1 & 5
\end{bmatrix}$.
- There are 3 columns and they are 4-dim vectors
- so $C(A)$ is a subspace $\mathbb R^4$
- but how big it is? is it the entire $\mathbb R^4$? No - we have only 3 vectors, so it’s at most $\mathbb R^3$
Since there are only 3 columns, in $A \mathbf x = \mathbf b$
- $\mathbf x \in \mathbb R^3$ and $\mathbf b \in \mathbb R^4$
- does it always have a solution? no: we have 4 equations and 3 unknowns
- there are many $\mathbf b$’s that can’t solve the system
- but there are some that can: they are linear combinations of the columns - so those $\mathbf b$ that are from $C(A)$
For example, the following can solve it:
- $\mathbf 0_4$, because $\mathbf x = \mathbf 0_3$ will solve it
- $\begin{bmatrix}
1
2
3
4
\end{bmatrix}$ - one of the columns, so $\mathbf x = \begin{bmatrix} 1
0
0
\end{bmatrix}$
if $\mathbf b \not \in C(A)$ there’s no way to solve the system
What’s the dimension of $C(A)$?
- $\text{dim } C(A) = r$ where $r$ -rank of $A$
- the easiest way to determine it - is calculate the number of pivot columns during Gaussian Elimination
- in this case, $\text{dim } C(A) = 2$ because the rank is 2 (the 3rd column is a linear combination of 1st and 2nd)