Isolation
A transaction is a sequence of updates to the database
- a transaction must be consistent
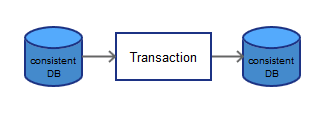
- we need to ensure that all the transactions run in isolation
- that is, while one transactions is running, no other transaction should see its intermediate results (which can be inconsistent)
Causes
Data Sharing (Concurrency)
- suppose that two transactions $T_1$ and $T_2$ are running at the same time
- $T_1$: give 10% rise to all programmers
- $T_2$: transfer some programmers to business analysts
Problem here:
- it should be either first $T_1$ and then $T_2$ or vice-versa
- otherwise there will be a lot of problems and unexpected results
- Concurrency Control techniques are used for that
Transaction Manager
- Transaction Manager is a component of a DBMS that has a scheduler
- The ‘‘scheduler’’ is responsible for creating an impressions that all transactions are run in isolation
Levels of Isolation
- Serializable (see Serializable Scheduling)
- …
- …
- No Isolation (actions of transactions can be executed in any order)