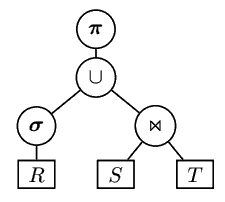
Logical Query Plan
In Relational Databases, Logical Query Plan - intermediate code in the Query Processing pipeline (typically a Relational Algebra expression)
- Essentially it’s an execution tree
- We evaluate it bottom-up
- Usually need to optimize it before executing to make the execution faster
Example
Suppose we have a Relational Algebra expression:
- $\pi_{A, B} \big(\sigma_{A = 5}(R) \cup (S \Join T) \big)$
-
- this defines the following execution tree
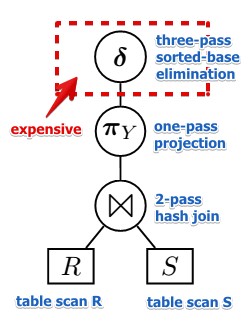
Physical Query Plan
A ‘‘Physical Query Plan’’ is the same as Logical Query Plan, but with specific algorithms assigned to each operation (node of the tree)
- I.e. it defines how exactly a query will be executed
- Query Result Size Estimation to estimate the size of physical operator’s output
- Physical Query Plan Optimization to select the best plan
Questions to consider
- What algorithms are available to do selections, joins, projections? These algorithms are called physical operators
- each physical operator has an associated cost - number of I/O operations (in I/O Model of Computation)
- It also highly depends on how data is stored
Example
- We just assign some operation to each node: