Cost-Complexity Pruning
Post-pruning algorithm for Decision Trees
- by Breiman, Olshen, Stone (1984)
Cost-Complexity Function
- need to optimize the cost-complexity function
-
$R_\alpha (T) = R(T) + \alpha \cdot f(T) $ where - $R(T)$ is the training/learning error - $f(T)$ a function that returns the set of leaves of tree $T$
- $\alpha$ is a Regularization parameter
- $R(T) = \sum_{t \in f(T)} r(t) \cdot p(t) = \sum_{t \in f(T)} R(t)$
- $\sum_{t \in f(T)} R(t)$ - sum of misclassification errors at each leaf
- $r(t) = 1 - \max_k p(C_k - t)$ - ‘‘misclassification rate’’
- $p(t) = \cfrac{n(t)}{n}$ with $n(t)$ being the # of records in node $t$ and $n$ - total # of records
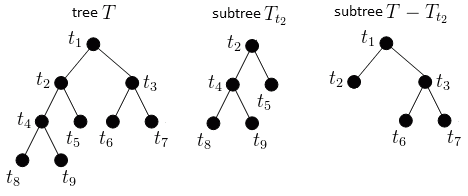
Pruning Subtrees
Subtrees:
Pruning a subtree $T_{t}$
- $R_\alpha(T - T_t) - R_\alpha(T)$ - variation of the cost-complexity function
- this is the cont-complexity when pruning subtree $T_t$
-
$R_\alpha(T - T_t) - R_\alpha(T) = R(T - T_t) - R(T) + \alpha ( f(T - T_t) - f(T) ) = R(t) - R(T_t) + \alpha ( 1 - f(T_t) )$ - let $\alpha’ = \cfrac{R(t) - R(T_t)}- variation is - null if $\alpha = \alpha’$
- negative if $\alpha < \alpha’$
- positive if $\alpha > \alpha’$
Algorithm
Pruning Algorithm:
- Initialization:
- let $T^1$ be the tree obtained with $\alpha^1 = 0$
- by minimizing $R(T)$
- Step 1
- select node $t \in T^1 $ that minimizes
- $g_1(t) = \cfrac{R(t) - R(T^1_t)} - let $t_1$ be this node
- let $\alpha^2 = g_1(t_1)$ and $T^2 = T^1 - T^1_{t_1}$
- select node $t \in T^1 $ that minimizes
- step $i$
- select node $t \in T^i $ that minimizes
- $g_i(t) = \cfrac{R(t) - R(T^i_t)} - let $t_i$ be this node
- let $\alpha^{i + 1} = g_i(t_i)$ and $T^{i+1} = T^i - T^i_{t_i}$
- select node $t \in T^i $ that minimizes
Output:
- a sequence of trees $T^1 \supseteq T^2 \supseteq \ … \ \supseteq T^k \supseteq \ … \ \supseteq { \text{root} }$
- a sequence of parameters $\alpha^1 \leqslant \alpha^2 \leqslant \ … \ \leqslant \alpha^k \leqslant \ … $
Choosing $\alpha$
The algorithm outputs $\alpha^1 \leqslant \alpha^2 \leqslant \ … \ \leqslant \alpha^k \leqslant \ … $
- need to choose some $\alpha \in [\alpha^k, \alpha^{k+1} )$
- let $\alpha \in [\alpha^k, \alpha^{k+1} )$
How to choose $\alpha$
- use Cross-Validation
- it’s the parameter that minimizes the validation error
- thus helps avoid Overfitting
Example
Example 1
Suppose we have the following tree:
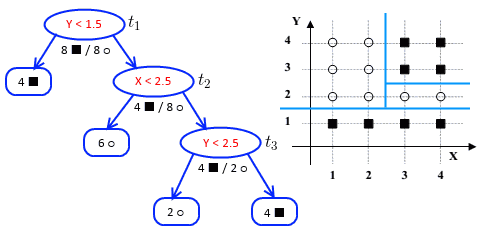
- we want to prune it
- we have 3 inner nodes where we can prune: $t_1 \equiv \text{root}, t_2, t_3$
Some formulas:
- $R(T_t)$ - training error of a subtree $T_t$ - a tree with root at node $t$
- $R(T_t) = \sum_{l \in f(T_t)} R(l)$ - sum of all training errors over all leaves
- $R_(t)$ - training error of node $t$
- $R_(t) = r(t) \cdot p(t)$
- $r(t)$ - misclassification error at this none (without considering the leaves)
- $p(t)$ - proportion of data items reached $t$ (i.e. # of items reached $t$ divided by # of training items)
-
$g(t) = \cfrac{R(t) - R(T_{T_t})} - $ f(T_t) - 1$ is the number of leaves to prune
’'’Iteration 1:’’’
- let $\alpha^{(1)} = 0$
| $t$ | $R_(t)$ | $R(T_t)$ | $g(t)$ | $t_1$ | $\cfrac{8}{16} \cdot \cfrac{16}{16}$ | $T_{t_1}$ - the entire tree
all leaves are pure
$R(T_{t_1}) = 0$ | $\cfrac{8/16 - 0}{4 - 1} = \cfrac{1}{6}$ || $t_2$ | $\cfrac{4}{12} \cdot \cfrac{12}{16} = \cfrac{4}{16}$
(there are 12 records, 4 $\blacksquare$ + 8 $\bigcirc$ ) | $R(T_{t_2}) = 0$ | $\cfrac{4/16 - 0}{3 - 1} = \cfrac{1}{8}$ || $t_3$ | $\cfrac{2}{6} \cdot \cfrac{6}{16} = \cfrac{2}{16}$ | $R(T_{t_3}) = 0$ | $\cfrac{2/16 - 0}{3 - 1} = \cfrac{1}{8}$ |
We want to find the minimal $g(t)$
- it’s $g(t_2)$ and $g(t_3)$
- in case of a tie, we choose the one that prunes fewer nodes
- i.e. $g(t_3)$
- so prune at $t_3$
- let $\alpha^{(2)} = 1/8$ (the min $g(t)$)
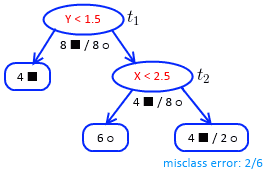
’'’Iteration 2:’’’
- in the tree now we have only candidates: $t_1$ and $t_2$
| $t$ | $R_(t)$ | $R(T_t)$ | $g(t)$ | $t_1$ | $\cfrac{8}{16} \cdot \cfrac{16}{16}$ | $\cfrac{2}{16}$ | $\cfrac{8/16 - 2/16}{3 - 1} = \cfrac{6}{32}$ | $t_2$ | $\cfrac{4}{12} \cdot \cfrac{12}{16}$ | $\cfrac{2}{16}$ | $\cfrac{4/16 - 2/16}{2 - 1} = \cfrac{1}{8}$ |
Find minimal $g(t)$:
- it’s $g(t_2) = 1/8$
- let $\alpha^{(3)} = 1/8$
- prune at $t_2$
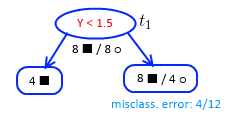
’'’Iteration 3:’’’
- only one candidate for pruning: $t_1$
- $\alpha^{(4)} = g(t_1) = \cfrac{8/16 - 4/16}{2 - 1} = \cfrac{1}{4}$
’'’Selecting the best’’’:
- we have these values: $\alpha^{(0)} = 0, \alpha^{(1)} = 1/8, \alpha^{(2)} = 1/8, \alpha^{(3)} = 1/4$
- by the theorem we want to find tree such $T$ that minimizes the cost-complexity function
- if $0 \geqslant \alpha < 1/8$, then $T_1$ is the best
- if $\alpha = 1/8$, then $T_2$ is the best
- if $1/8 < \alpha < 1/4$, then $T_3$ is the best
- if $1/8 < \alpha < 1/4$, then $T_3$ is the best
- to choose $\alpha$ use Cross-Validation
Example 2
From IT4BI 2013 year exam:
- see here